News
GPT-4 Shows Promise in Writing Radiology Reports
GPT-4 outperforms other large language models -- and, occasionally, human doctors -- in multiple radiology tasks, according to a new Microsoft research paper.
The paper, which Microsoft presented at this week's Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, is part of Project MAIRA, an effort by Microsoft researchers to find ways to improve radiology using multimodal AI. "Multimodal" refers to the ability of a tool to understand and process unstandardized data in different formats, including images, code and text.
After putting GPT-4 through its paces, researchers found the model performed as well as, or better than, other multimodal LLMs, including GPT-3.5. For some tasks, such as "temporal sentence similarity" and "natural language inference," it demonstrated a 10 percent improvement over previous models.
It also demonstrated the ability to write more logically structured radiology reports, which generally combine data from X-rays, patient medical histories and a doctor's own observations. Such reports don't typically follow a standard structure, making them difficult to read or use for research.
Notably, GPT-4 occasionally performed better than "experienced radiologists" when it came to summarizing radiology reports (as shown below).
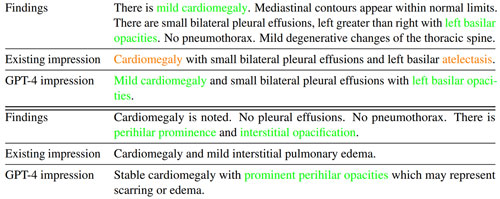 [Click on image for larger view.]
Figure 1. Examples where GPT-4 findings summaries are favored over existing manually written ones on the Open-i dataset. In both examples, GPT-4 outputs are more faithful and provide more complete details on the findings. (Source: Microsoft)
[Click on image for larger view.]
Figure 1. Examples where GPT-4 findings summaries are favored over existing manually written ones on the Open-i dataset. In both examples, GPT-4 outputs are more faithful and provide more complete details on the findings. (Source: Microsoft)
Efforts to discover more ways generative AI can improve medical imaging are manifold. The Mayo Clinic, for instance, is currently at work developing a massive medical LLM comprising CT scans from thousands of patients to help detect cancers. ;
Microsoft's researchers described its findings "encouraging" but requiring "further validation through extensive research and clinical trials."
"Nonetheless," they concluded, "the emergence of GPT-4 heralds an exciting future for radiology."